Nigeria has taken a significant step to protect its telecommunications infrastructure by setting up a Joint Standing Committee on the Protection of Fiber Optic Cables.
This initiative, spearheaded by the Federal Ministry of Works (FMoW) and the Federal Ministry of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy (FMoCIDE), aims to curb the rampant fibre cuts that have disrupted telecom services nationwide.
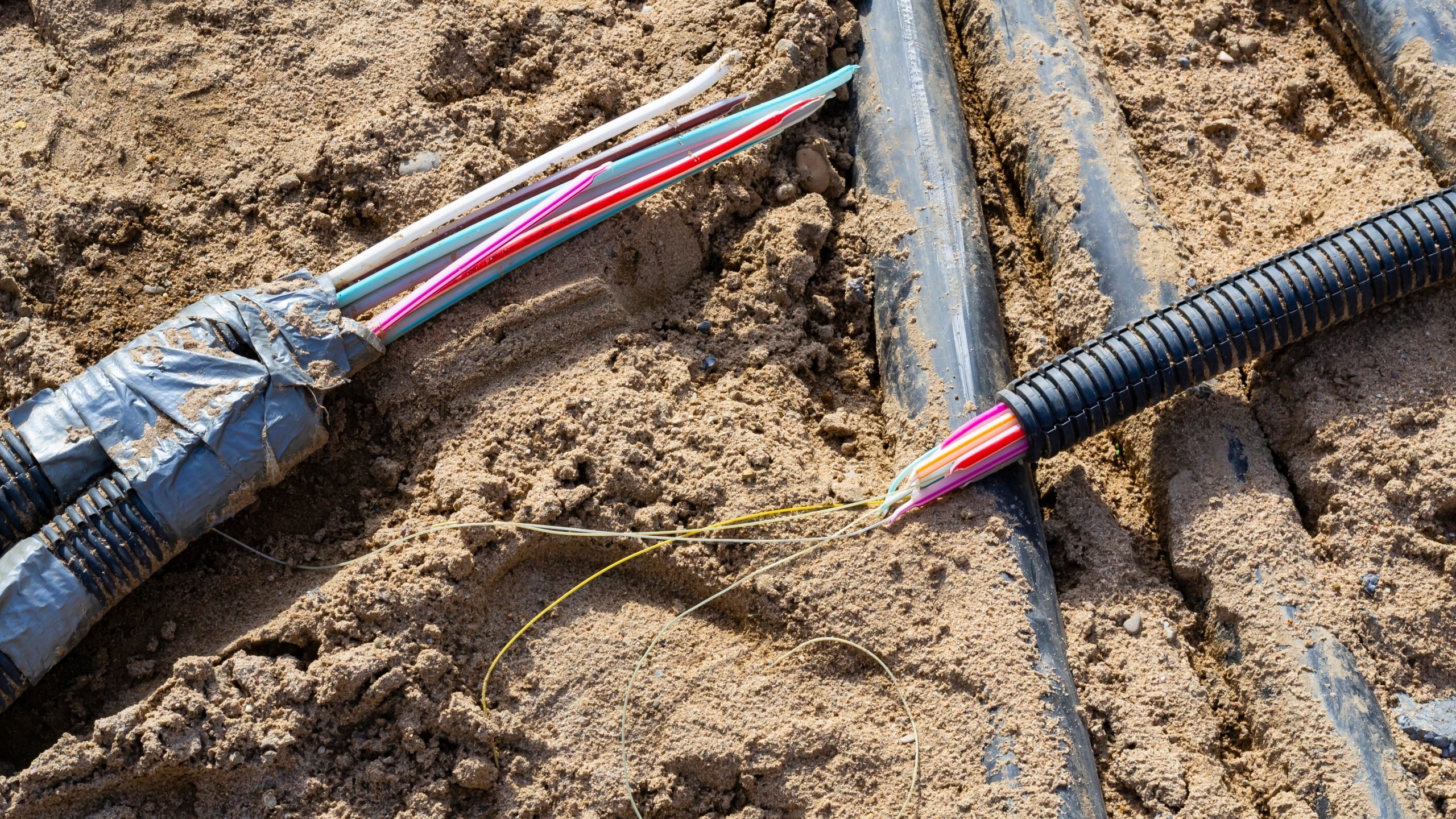
Frequent damage to fibre optic cables, often caused by road construction and maintenance activities, has led to severe service interruptions, affecting millions of telecom users. In 2024 alone, Nigeria recorded over 50,000 fibre cuts, with around 30,000 attributed to road construction projects.
These incidents contribute to major network outages, such as the February 2024 nationwide MTN outage, which left subscribers disconnected for hours.
The new committee, inaugurated on February 18, 2025, comprises representatives from both ministries and the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC). It will serve as a coordinating body to develop strategies for minimising cable damage and establishing clear communication protocols between telecom operators and construction firms.
Permanent Secretary at the Federal Ministry of Works, Engr. Olufunso Adebiyi stressed that the committee’s primary role is to develop standardised engagement procedures to ensure fibre optic infrastructure is safeguarded before, during, and after road construction projects. This includes creating instant communication mechanisms between telecom firms and road contractors, ensuring that fibre placement is factored into road design and construction planning, and collaborating with Federal Controllers of Works to protect fibre infrastructure nationwide.
Additionally, Engr. Farouk Yusuf, Permanent Secretary at FMoCIDE, highlighted the critical role of fibre optics in Nigeria’s digital economy. Reliable fibre networks underpin both fixed and mobile broadband services, enabling seamless connectivity, economic growth, and technological innovation.
NCC Chief Executive Officer, Dr. Aminu Maida, stressed that reducing fibre cuts will improve service quality, lower maintenance costs, and enable faster broadband expansion. He acknowledged that the lack of an efficient coordination mechanism between road contractors and telecom firms has been a key factor behind rising fibre cuts.
“Every time a fibre cut occurs, Nigerians experience service disruptions. Operators are forced to invest heavily in redundant routes and repair work. If we can prevent these avoidable incidents, telecom companies can redirect funds toward expanding network infrastructure,” Dr. Maida explained.
Going forward, the government has committed to incorporating fibre optic ducting into new road infrastructure projects, ensuring that telecom networks remain resilient. The committee will meet regularly to evaluate progress, address emerging challenges, and refine its strategy.
Source: www.techpoint.africa