NVIDIA unveiled partnerships with T-Mobile, MITRE, Cisco, ODC, a portfolio company of Cerberus Capital Management, and Booz Allen Hamilton on the research and development of artificial intelligence (AI)-native wireless network hardware, software and architecture for 6G.
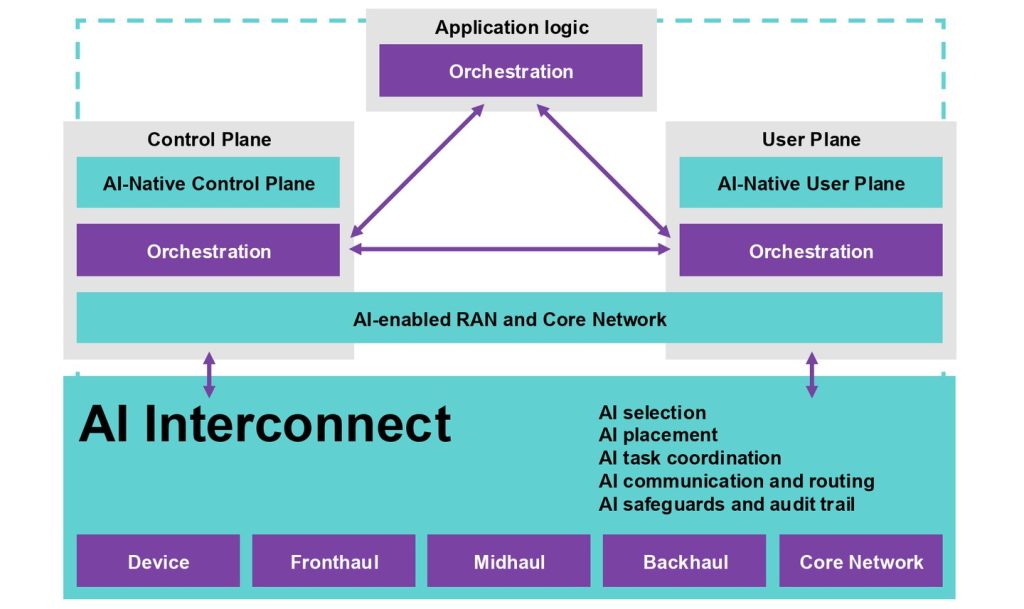
Next-generation wireless networks must be fundamentally integrated with AI to connect hundreds of billions of phones, sensors, cameras, robots and autonomous vehicles. AI-native wireless networks will provide enhanced services for billions of users and set new standards in spectral efficiency — the rate at which data can be transmitted over a given bandwidth. They will also offer performance and resource utilisation while creating new revenue streams for telecommunications companies.
“Next-generation wireless networks will be revolutionary, and we have an unprecedented opportunity to ensure AI is woven in from the start,” said Jensen Huang, the founder and CEO of NVIDIA. “Working with leaders in the field, we’re building an AI-enhanced 6G network that achieves extreme spectral efficiency.”
Open ecosystems drive innovation
Research-driven breakthroughs harnessing the power of AI are necessary to maximise the performance and benefits of AI-native wireless networks. To drive innovation, NVIDIA is collaborating with telco and research leaders to develop an AI-native wireless network stack based on the NVIDIA AI Aerial platform, which provides software-defined radio access networks (RANs) on the NVIDIA accelerated computing platform.
Developers across the globe are building AI-RAN as a precursor to AI-native 6G wireless networks. AI-RAN is a technology that brings AI and RAN workloads together on one platform and embeds AI into radio signal processing.
To deliver enhanced spectral efficiency and lower operational complexity and costs, AI will be fully embedded into the network stack’s software and hosted over a unified accelerated infrastructure, capable of running both network and AI workloads. Also at the solution’s core will be end-to-end security and an open architecture to foster rapid innovation.
T-Mobile and NVIDIA will expand their AI-RAN Innovation Centre collaboration announced last year with the goal of providing additional research-based concepts for AI-native 6G network capabilities, working alongside these new industry collaborators.
“This is an exciting next step to the AI-RAN Innovation Centre efforts we began last September at our Capital Markets Day in partnership with NVIDIA,” said Mike Sievert, the CEO of T-Mobile. “Working with these additional industry leaders on research to natively integrate AI into the network as we begin the journey to 6G will enable the network performance, efficiency and scale to power the next generation of experiences that customers and businesses expect.”
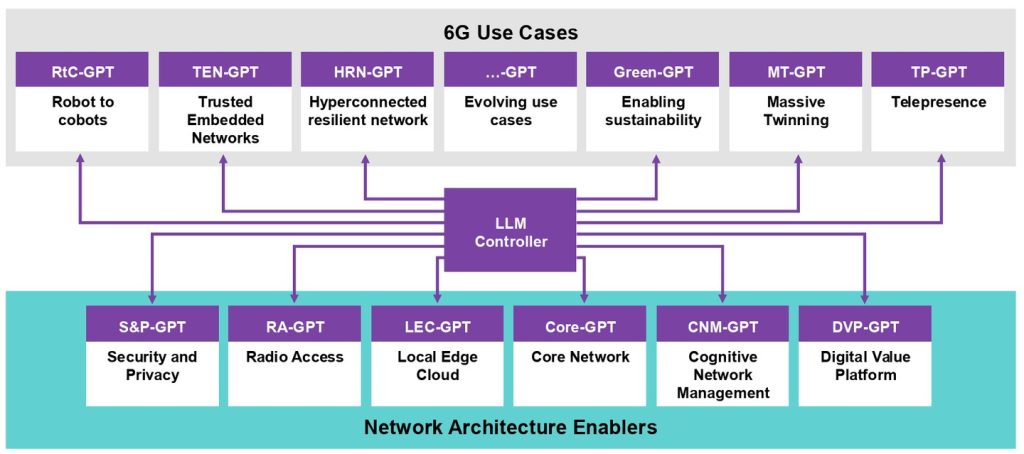
As the founding research partner, MITRE, a not-for-profit research and development organisation, will research, prototype and contribute open, AI-driven services and applications, such as for agentic network orchestration and security, dynamic spectrum sharing and 6G-integrated sensing and communications.
“MITRE is working with NVIDIA to help make AI-native 6G a reality,” said Mark Peters, the president and CEO of MITRE. “By integrating AI into 6G in the beginning, we can solve a wide range of problems, from enhancing service delivery to unlocking required spectrum availability to fuel wireless growth. Through all of our collaborations with NVIDIA, we look forward to creating impact in 6G, AI, simulation, transportation and more.”
Cisco plans to take a lead position in this collaboration as the provider of mobile core and network technologies and will tap into its existing service provider reach and expertise.
“With 6G on the horizon, it’s critical for the industry to work together to build AI-native networks for the future,” said Chuck Robbins, the chair and CEO of Cisco. “Cisco is at the forefront of developing secure infrastructure technology for AI, and we are proud to work with NVIDIA and the broader ecosystem to create an AI-enhanced network that improves performance, reliability and security for our customers.”
ODC, a portfolio company of Cerberus Capital Management, L.P., will deliver cutting-edge layer 2 and layer 3 software for distributed and centralised units of virtual RAN as part of the AI-native radio access stack. Tapping into decades of experience in large-scale mobile systems, ODC is pioneering next-generation AI-native 5G open RAN (ORAN), surpassing existing networks and paving the way for 6G evolution.
“The mobile industry has always taken advantage of advances in other technology fields, and today, no technology is more central than AI,” said Shaygan Kheradpir, the chairman of the advisory board of ODC. “ODC is at the forefront of developing and deploying AI-native ORAN 2.0 networks, enabling service providers to on-ramp seamlessly from 5G to 6G by taking advantage of the vast AI ecosystem to redefine the future of connectivity.”
As a leader in AI and cybersecurity to the federal government, Booz Allen will develop AI RAN algorithms and secure the AI-native 6G wireless platform. Its NextG lab will conduct functional, performance integration and security testing to ensure the resiliency and security of the platform against the most sophisticated adversaries. The company will lead field trials for advanced use cases such as autonomy and robotics.
“The future of wireless communications starts today, and it’s all about AI,” said Horacio Rozanski, the chairman and CEO of Booz Allen. “Booz Allen has the technologies to make AI-native 6G networks a reality and revolutionise secure communications for an entirely new generation of intelligent platforms and applications.”
Expanded aerial research portfolio
These collaborations build on NVIDIA’s AI-RAN and 6G research ecosystem, supported by advancements in the NVIDIA Aerial research portfolio for developing, training, simulating and deploying AI-native wireless innovations.
New additions to the NVIDIA Aerial Research portfolio, also announced today, include the Aerial Omniverse Digital Twin Service, the Aerial Commercial Test Bed on NVIDIA MGX, NVIDIA Sionna 1.0 — building on the open-source Sionna library, which has nearly 150,000 downloads since its launch in 2022 — and the Sionna Research Kit on the NVIDIA Jetson accelerated computing platform.
The NVIDIA Aerial Research portfolio serves over 2,000 members through the NVIDIA 6G Developer Program. Industry leaders and more than 150 higher-education and research institutions from the U.S. and around the world are harnessing the platform to accelerate 6G and AI-RAN innovation — paving the way for AI-native wireless networks.