At the intersection of truth-seeking and technology coverage, Rosemond Akuorkor Adjetey has carved a formidable path. Her compelling reportage earned her the Print and Online sub-category award under the EMIs category at the first-ever Technology Industry Media Excellence Awards (TIMEA), held in Accra.
Continue readingSuleiman Mustapha Honoured at TIMEA Awards for Excellence in Print & Online Reporting
Championing Economic Insight Through Fearless Journalism
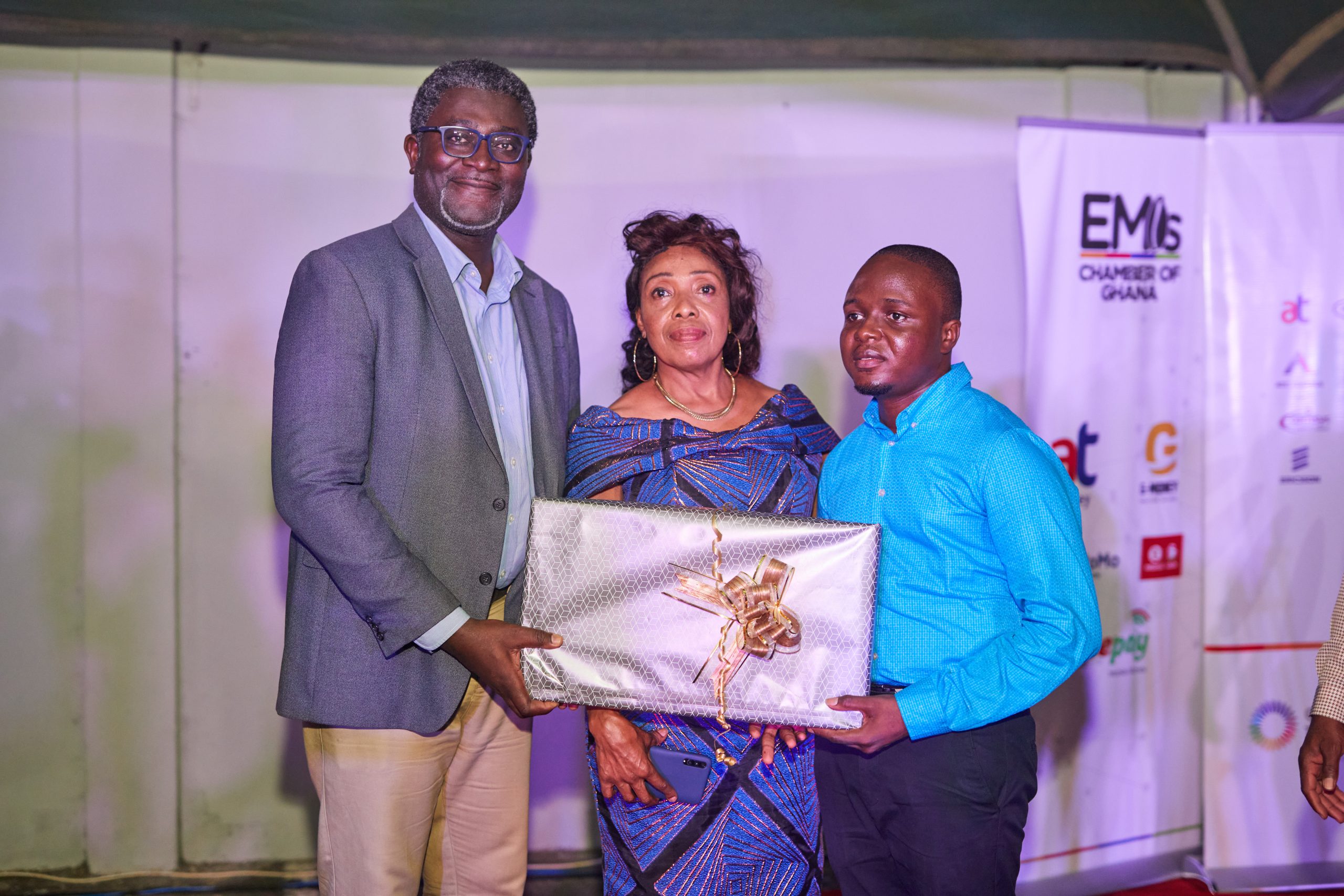
At the heart of Ghana’s business and economic reportage lies the enduring voice of Suleiman Mustapha, the distinguished Special Correspondent of the Graphic Communications Group Limited. At the inaugural Technology Industry Media Excellence Awards (TIMEA), Suleiman was honoured as the winner in the Print and Online sub-category under the Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) category.
With a keen eye for unraveling complex market dynamics and a penchant for precision, Suleiman’s winning stories offered fresh clarity on the inner workings of Ghana’s telecommunications and digital infrastructure sectors. His coverage deconstructed industry reforms, investment flows, and corporate strategies—connecting the dots for policy actors, investors, and the everyday reader.
No stranger to recognition, Suleiman previously earned the prestigious GJA Business and Financial Journalist of the Year (2018). At TIMEA, his investigative rigor and thought leadership once again earned industry-wide respect.
As a leading advocate for responsible financial journalism, Suleiman currently serves as the President of the Journalists for Business Advocacy (JBA). His editorial work continues to set benchmarks for integrity, insight, and transformative impact.
In appreciation of his exceptional contribution, Suleiman received a laptop and a citation certificate, presented during the awards event attended by media luminaries, Chamber executives, and representatives from Ghana’s telecom and fintech landscape.
“Suleiman’s writing demystifies the most complex economic themes, making them accessible and actionable for public good,” noted one TIMEA judge.
His TIMEA win reaffirms the essential role that in-depth, policy-literate journalism plays in shaping the future of Ghana’s digital economy.
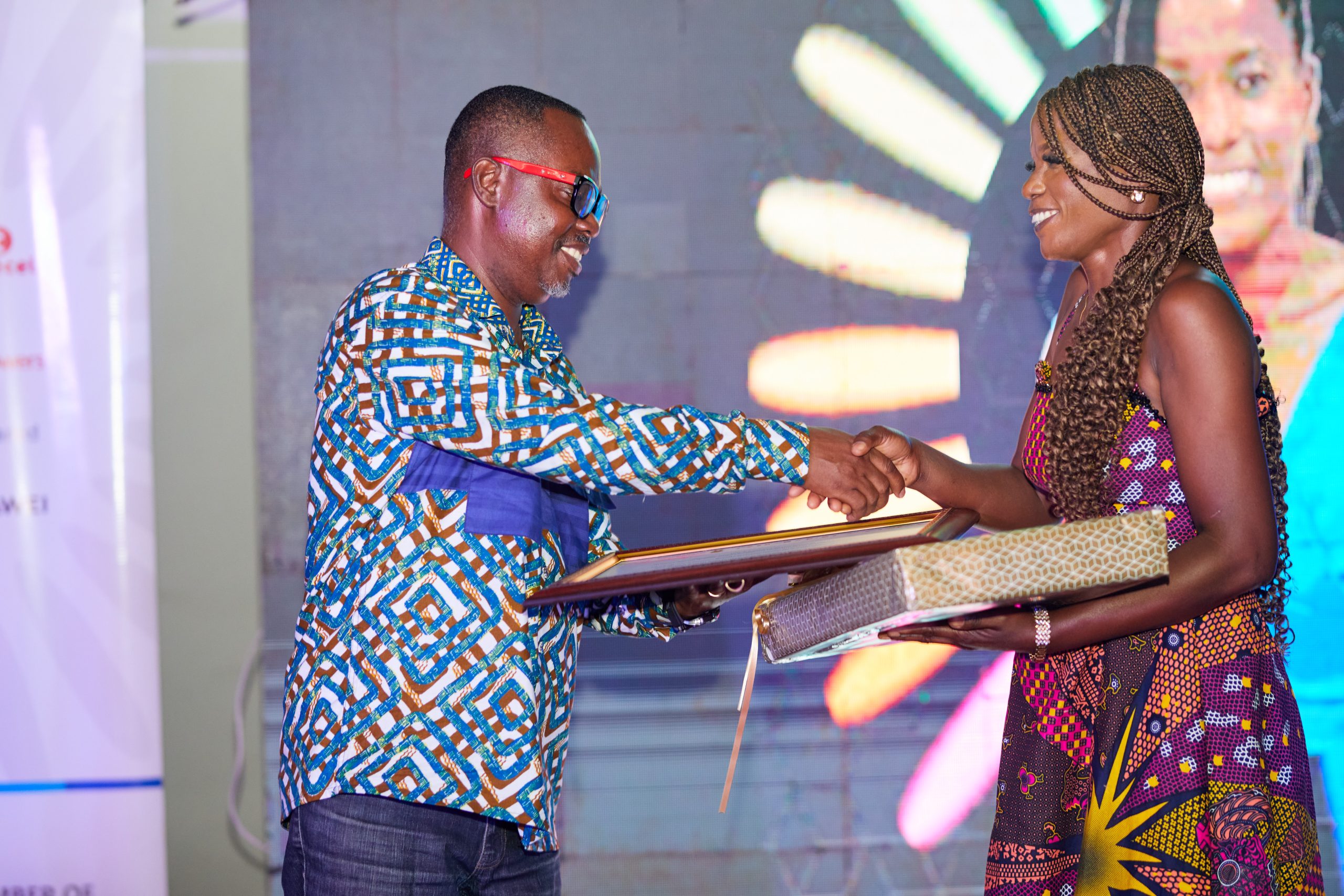
Ivan Heathcote-Fumador Crowned Overall Winner at Inaugural TIMEA Awards
A Visionary Beyond Sight, Championing Digital Inclusion
In a resounding testament to courage, depth, and journalistic brilliance, Ivan Heathcote-Fumador of Ultimate FM, a subsidiary of the EIB Network, emerged the overall winner at the maiden edition of the Technology Industry Media Excellence Awards (TIMEA), held in Accra.
Ivan was adjudged winner in the Broadcast sub-category under the Electronic Money Issuers (EMIs) category, distinguishing himself through exceptional reporting that merges inclusivity with innovation. His work sheds critical light on how digital finance and technology are reshaping underserved communities—particularly from the lens of accessibility and equality.
A solutions-focused journalist with over a decade of experience, Ivan’s beat spans the intersection of disability rights, gender advocacy, digital economy, and governance. His nuanced coverage consistently elevates voices often sidelined in mainstream tech discourse. Though visually impaired, his storytelling is unclouded—probing, principled, and profoundly impactful.
Held on Friday, December 13, 2024, the TIMEA Awards brought together thought leaders from across Ghana’s telecommunications and fintech ecosystem, celebrating journalists whose reporting fuels public understanding and sector advancement.
As overall winner, Ivan received a brand-new laptop and a citation from the Ghana Chamber of Telecommunications and the EMIs Chamber of Ghana, co-organisers of the initiative.
“Ivan’s stories not only inform, but also inspire the entire industry to do better—for everyone,” remarked a Chamber executive during the ceremony.
With his signature depth and humanity, Ivan continues to prove that while he may lack sight, his vision leads the way for inclusive, responsible tech journalism in Ghana and beyond.
MTN Launches Digital Hub in South Sudan IDP Camp to Bridge Connectivity Gap
Source: News Ghana | June 21, 2025
MTN South Sudan has inaugurated a digital hub at the Mangateen internally displaced persons (IDP) camp in Juba, offering free internet access, solar-powered computers, and digital learning resources to one of the country’s most underserved communities.
The initiative, launched under the telecom giant’s annual #21DaysOfY’elloCare corporate social responsibility campaign, aims to promote digital inclusion in post-conflict zones where infrastructure and access to technology remain severely limited.
MTN South Sudan CEO Mapula Bodibe described the hub as a gateway to education and economic empowerment for displaced populations. “Connectivity is no longer a luxury—it’s a lifeline. This hub provides tools that enable learning, entrepreneurship, and access to opportunity,” she said.
The project addresses a critical digital divide in South Sudan, where many communities still lack basic internet access despite growing reliance on digital tools for recovery and reintegration.
Similar efforts across MTN’s African footprint highlight how private sector investment can complement humanitarian interventions, providing long-term, sustainable support in fragile and underserved regions.
Source: News Ghana | June 21, 2025
Telecel Ghana CEO Calls for Innovation-Friendly Tech Regulation at Africa Rising Symposium
Source: News Ghana | June 20, 2025
Telecel Ghana CEO Patricia Obo-Nai has called on African regulators and industry players to embrace progressive, collaborative approaches to emerging technologies—stressing that resistance to innovation risks holding back the continent’s digital transformation.
Speaking at the Africa Rising Symposium 2025 in Accra, Obo-Nai urged policymakers to align regulatory frameworks with rapid advancements in satellite connectivity, mobile finance, and cryptocurrency. “You cannot stop innovation,” she said. “What matters is understanding customer expectations and working with regulators to meet them.”
Highlighting satellite technology as a game-changer for last-mile connectivity, Obo-Nai noted that direct-to-device capabilities can bypass traditional infrastructure and extend coverage to underserved communities. Yet, in Ghana, current regulations prohibit direct satellite-to-handset communication, mandating signal routing through terrestrial switches—a policy she believes urgently needs review.
Turning to fintech, she described Telecel Ghana’s evolving role in the digital economy—from facilitating cross-border payments with banks to developing seamless wallet-to-wallet services. On digital assets, she urged a regulatory posture of enablement rather than prohibition: “People have chosen how they want to invest. Our responsibility is to create an environment for safe participation.”
Her remarks come at a time when African countries are navigating the complex balance between enabling innovation and exercising regulatory control, especially in the fast-moving financial technology and connectivity space.
The Africa Rising Symposium convened thought leaders, policymakers, and tech stakeholders to explore the continent’s digital future—one that, according to Obo-Nai, must be built on openness, inclusion, and regulatory foresight.
Source: News Ghana | June 20, 2025
Helios Towers Marks 15 Years of Driving Ghana’s Digital Infrastructure
Source: Myjoyonline
Helios Towers has commemorated 15 years of transformative work in Ghana’s telecommunications landscape with a high-profile gala at the Grand Arena of the Accra International Conference Centre—celebrating a legacy of connectivity, innovation, and inclusion.
Launched in Ghana in 2010, Helios Towers has since grown into one of Africa’s leading independent telecom infrastructure providers. The company has enabled mobile coverage for more than 18 million Ghanaians, established over 1,096 tower sites nationwide, and taken industry leadership in green energy innovation with more than 400 solar-powered towers deployed.
“Ghana is where our story began—and it remains the heartbeat of our operations,” said Kweku Frempong, Managing Director of Helios Towers Ghana. “This milestone is a tribute to resilience, innovation, and the impact that comes from investing in people and potential.”
The celebratory event brought together key stakeholders, including the Minister for Communications and Digitalisation, Hon. Sam George, and Board Chairman Sir Sam Jonah, alongside telecom executives, government officials, and community partners.
From its beginnings as a single-market operator, Helios Towers has expanded its footprint to over 14,000 sites across nine markets in Africa and the Middle East—including Tanzania, DRC, Senegal, South Africa, and Oman. The company credits its growth to strategic local partnerships and a deeply rooted Ghanaian workforce, with 100% of Helios Towers Ghana employees being Ghanaian and 22% of them women—an impressive feat in a male-dominated field.
Helios Towers Ghana has also made significant investments in rural connectivity, with more than 290 rural sites and nearly $1 million directed toward staff training and upskilling. Its green energy drive is exemplified by the countrywide solar rollout, underscoring its commitment to sustainability.
Now entering its next chapter, Helios Towers continues to position itself as a key enabler of Ghana’s digital future.
Source: Myjoyonline
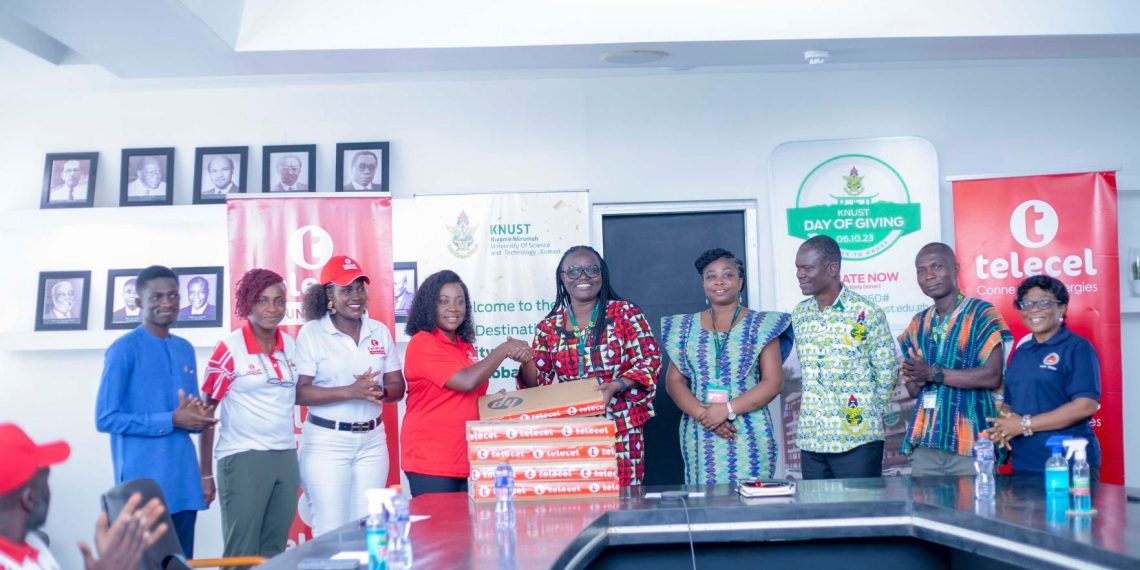
Telecel Ghana Donates 100 Laptops to KNUST to Empower Needy Students
Source: Citi Newsroom
As part of its commitment to digital inclusion, the Telecel Ghana Foundation has donated 100 brand-new laptops to the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) to support underprivileged students.
The donation, made under the Foundation’s Connected Learning pillar, is the second to the university’s Support One Needy Student with One Laptop (SONSOL) initiative. In 2021, Telecel provided 200 laptops in response to KNUST’s appeal to bridge the digital divide affecting thousands of students.
Speaking at the handover ceremony in Kumasi, Chief Executive Officer of Telecel Ghana and KNUST alumna, Ing. Patricia Obo-Nai, reiterated the telco’s pledge to support equitable access to learning tools.
“With these laptops, more students will participate fully in virtual learning, collaborate on group projects, and take charge of their academic futures,” she said, emphasizing the company’s focus on digital empowerment.
KNUST Vice-Chancellor Professor Mrs. Rita Akosua Dickson expressed deep appreciation, noting that the support would uplift brilliant but disadvantaged students facing barriers in the digital learning space.
“This investment will unearth the potential of transformational leaders who would otherwise be left behind due to economic hardship. Its impact will extend well beyond the immediate beneficiaries,” she stated.
Student leadership echoed this sentiment. SRC Vice President Samuel Afful remarked that the intervention offers both relief and dignity to many students who previously relied on borrowed or faulty devices.
The donation coincides with Telecel Ghana’s Ashanti Month—an annual celebration that reaffirms the company’s long-standing partnerships in the region and its dedication to community development through digital access.
Source: Citi Newsroom
MTN MoMo Underscores Commitment to Digital Financial Security
Source: GNA | Edited by Dennis Peprah
MTN Mobile Money (MoMo) Limited has reaffirmed its commitment to strengthening digital financial security as it continues to enhance the safety of online transactions for its growing user base.
Speaking to journalists in Dormaa-Ahenkro in the Bono Region, Razak Issaka Ali, Chief Commercial Officer of MTN MoMo, urged users to download the updated MTN MoMo App, which integrates enhanced security features including two-factor authentication and biometric verification.
“The App is easier, faster, and built with top-tier security. We’re constantly updating it to safeguard our customers,” Mr. Ali noted.
His comments followed a customer appreciation ceremony where 21-year-old mobile phone repairer Emmanuel Ansu Gyeabour was recognised as the platform’s one millionth MoMo App user. Gyeabour received a GHS10,000 cash prize along with branded souvenirs.
With over 17 million users nationwide, MoMo remains a key enabler of Ghana’s digital economy—supporting payments, savings, investments, and financial inclusion. CEO of MTN MoMo, Haruna Shaibu, credited the service for enhancing transaction speed, business convenience, and economic growth.
While applauding MTN’s efforts, Mr. Gyeabour encouraged the telecom provider to further improve network coverage in the area.
MTN MoMo continues to serve as a digital financial backbone for millions across Ghana, positioning itself as a leader in secure and accessible mobile transactions.
Source: GNA | Edited by Dennis Peprah
GSMA Urges Mobile Industry to Double Emissions Cuts to Meet Net Zero Goals
By Amiya Johar | Source: Mobile Net Zero Report via GSMA
The GSMA is calling on mobile network operators to accelerate their decarbonisation efforts, warning that current progress falls short of the trajectory required to reach net zero emissions by 2050.
According to the mobile industry body’s latest Mobile Net Zero report, operators achieved an 8% reduction in operational emissions between 2019 and 2023, even as global mobile connections rose by 9% and data consumption quadrupled. The findings were released ahead of MWC Shanghai.
Despite this progress, the GSMA cautions that the pace of emissions reduction must increase to 7.5% annually through to 2030—more than twice the current rate. Preliminary 2024 data shows a 4.5% drop, indicating improvement but still below target.
Renewable energy uptake played a significant role in the sector’s emissions decline, with 37% of electricity sourced from renewables in 2023—up from just 13% in 2019. This shift reportedly prevented around 16 million tonnes of carbon emissions. Regional leaders include Europe, which cut operator emissions by 56% since 2019, followed by North America (44%) and Latin America (36%). For the first time, China recorded a 4% drop in operator emissions, spurred by a sharp increase in clean energy use.
Still, GSMA flags Scope 3 emissions—those generated across supply chains and manufacturing—as a key challenge, accounting for two-thirds of the sector’s carbon footprint. These value chain emissions remain a critical focus area for operators aligning with science-based targets.
Operators are increasingly turning to energy-efficient infrastructure, solar power, battery storage, and the phasing out of diesel-based and legacy networks. But GSMA stresses that stronger policy environments and expanded renewable energy access are essential to meet global sustainability ambitions.
Consumer trends also signal growing momentum for sustainability. Nearly 90% of surveyed users are open to refurbished devices, a market expected to reach $150 billion by 2027.
“This industry isn’t greenwashing or greenwishing—it’s green acting,” said Steven Moore, GSMA’s Head of Climate Action. “But to stay on track, we need faster progress, firmer policy support, and deeper collaboration across the ecosystem.”
By Amiya Johar | Source: Mobile Net Zero Report via GSMA
Orange Egypt and Huawei Deepen Partnership to Accelerate 5G Rollout
Orange Egypt, in partnership with Chinese tech giant Huawei, is intensifying efforts to expand 5G connectivity across Egypt—aiming to boost both consumer and enterprise access to next-generation digital services.
The collaboration is set to catalyse the adoption of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). The companies describe the 5G push as foundational to developing smart ecosystems across sectors, from smart cities to the Internet of Things (IoT).
Central to this initiative is the deployment of Huawei’s E-band microwave technology, operating within the 71–76 GHz and 81–86 GHz frequency ranges. This solution offers ultra-high throughput and low-latency backhaul capabilities, particularly vital for urban zones with dense traffic and rural areas lacking fibre infrastructure.
Huawei’s Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) solutions for Radio Access Networks are also being leveraged to enhance Orange Egypt’s 5G performance. These technologies are engineered to deliver higher spectral efficiency, improved network capacity, and robust service quality—even in bandwidth-intensive environments. Use cases span ultra-HD video streaming to immersive AR/VR experiences.
“With our advanced 5G solutions, we are enabling the next generation of mobile networks to deliver faster, more reliable and energy-efficient services,” said Mohamed Youssef, Key Account Executive at Huawei Egypt. “This partnership underscores Huawei’s dedication to helping operators meet the growing demand for high-speed, sustainable connectivity.”
The partnership signals a significant step toward strengthening Egypt’s digital infrastructure, broadening access to the digital economy, and future-proofing telecommunications services.
Source: ITWeb