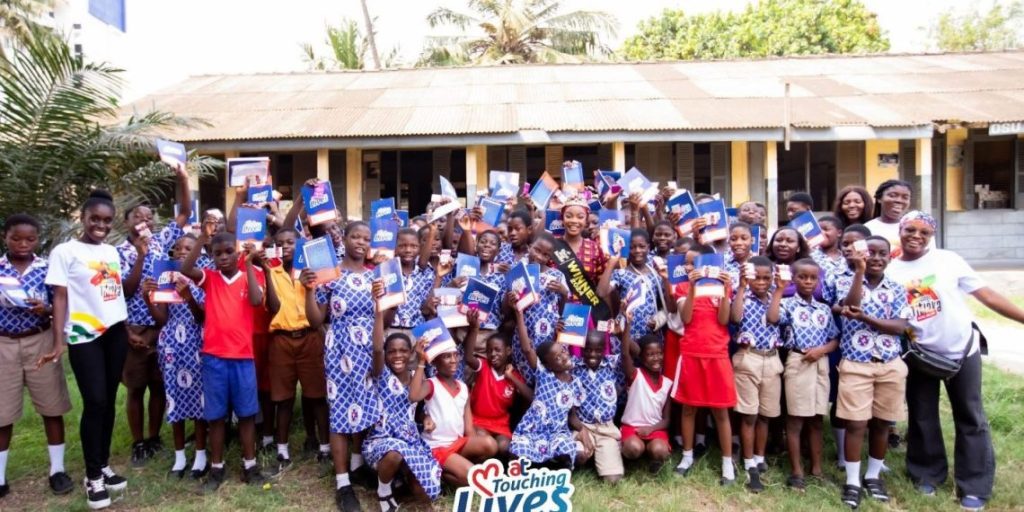
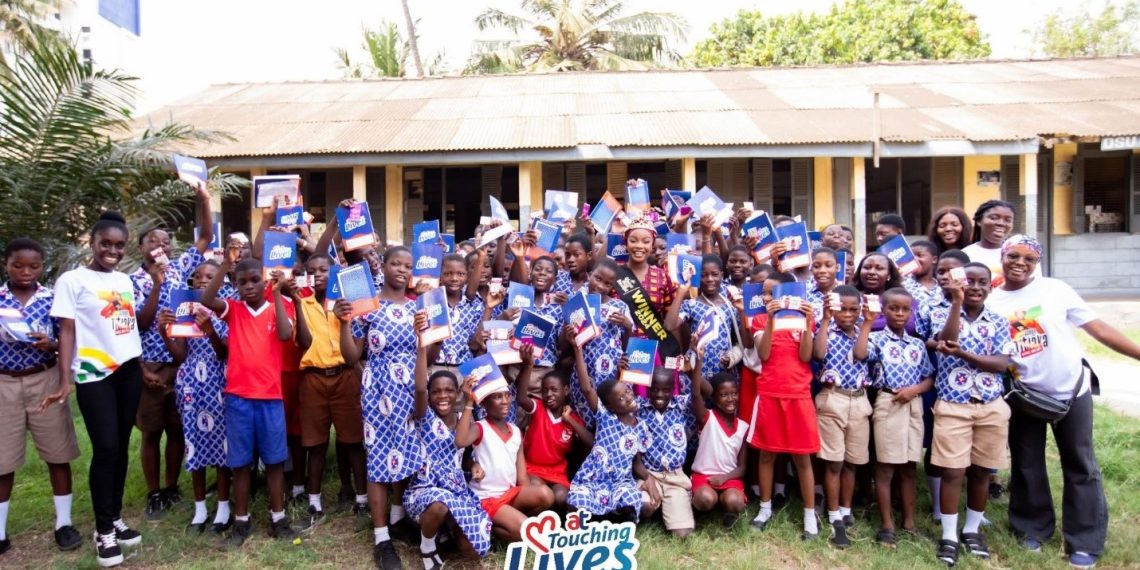
As part of its Month of Love celebration, AT Touching Lives, the corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiative of AT Ghana, partnered with Ghana’s Most Beautiful (GMB) 2024 Queen Nihad Titiaka Oases Ibrahim – Titiaka on the “Sweet Smiles” initiative to mark National Chocolate Day with pupils of Khairiya Islamic and Osu Salem Basic Schools.
Interacting with the pupils Queen Titiaka addressed the current effects of climate change, highlighting its adverse effects on cocoa farming and the need for proactive measures such as tree planting, recycling, proper waste management, and community education on climate action
She further promised to reward pupils who plant the most trees before her next visit. She also urged them to focus on their education, stressing that it is the key to unlocking future opportunities.
Speaking on behalf of AT Ghana, Mrs. Felicia Evame Thornhill, Community Engagement Manager of AT (formerly of AirtelTigo), reaffirmed AT’s commitment to education and innovation. She encouraged pupils to explore STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields to develop innovative solutions for climate-related challenges.
“There is a direct link between STEM education, climate change, and cocoa farming. As we celebrate National Chocolate Day, it is important to recognize the impact of climate change on cocoa production. I encourage you to explore STEM fields to contribute to sustainable solutions for our agricultural sector,” she stated.
The school authorities of Khairiya Islamic and Osu Salem Basic Schools expressed their deep gratitude for the initiative. The headmistress of Khairiya Islamic Basic School, highlighted Queen Titiaka’s achievements as an inspiration, particularly for young Muslim girls, encouraging them to pursue their dreams through education and perseverance.
A class 4 pupil from Osu Salem Basic School, Muniratu Mohammed shared her excitement, saying, “I never knew climate change could affect cocoa farming. I have learned that planting more trees can help protect our cocoa so I will ensure to plant more trees and share this knowledge with my friends and family.”
The event was attended by notable figures, including the Zongo Chief of Adabraka, PTA representatives from both schools, members of Queen Titiaka’s team, and employees of AT Ghana.
The even wasn’t marked to not only celebrate chocolate day but also educate students on climate change and its impact on cocoa farming, encouraging them to adopt sustainable environmental practices.